Documentation
We are glad to have you here! In our documentation you’ll find everything you need to work with Forms Bridge.
Forms Bridge is a powerful tool to integrate your WordPress forms with third party systems over HTTP requests. The approach of this plugin is to escape from closed solutions and to bring to the user a set of tools to make him autonomous to set up his own integrations. At the same time, “With great power comes great responsibility” and basic knowledge of how HTTP and REST APIs works is required.
You can complement this documentation with the tutorials of the blog. If you miss something or think a new tutorial may be interesting for the community, send us a message through the contact form.
Getting started
This guide is an introduction to the Forms Bridge plugin for WordPress. With various examples, this tutorial explains how to setup a bridge that connects WordPress forms with remote systems over the network.
Install an integration
Forms Bridge is a system to bridge WordPress forms with backends over HTTP requests. Forms Bridge itself does not build forms, but is capable to work with the most used WordPress form builder plugins.
You can install Forms Bridge without any integration installed on your WordPress instance, but without one of the supported ones, this plugin is useless. So lets start by installing one of the supported plugins:
For this example we will work with Contact Form 7 and the default contact form that comes out of the box with it.
Set up a backend
The first step to establish a bridge between your WordPress forms and your backend or service, is to register this backend / service connection. On the admin panel, go to Settings > Forms Bridge to open the plugin’s settings page. If it’s your first time here, you will find a screen like this:
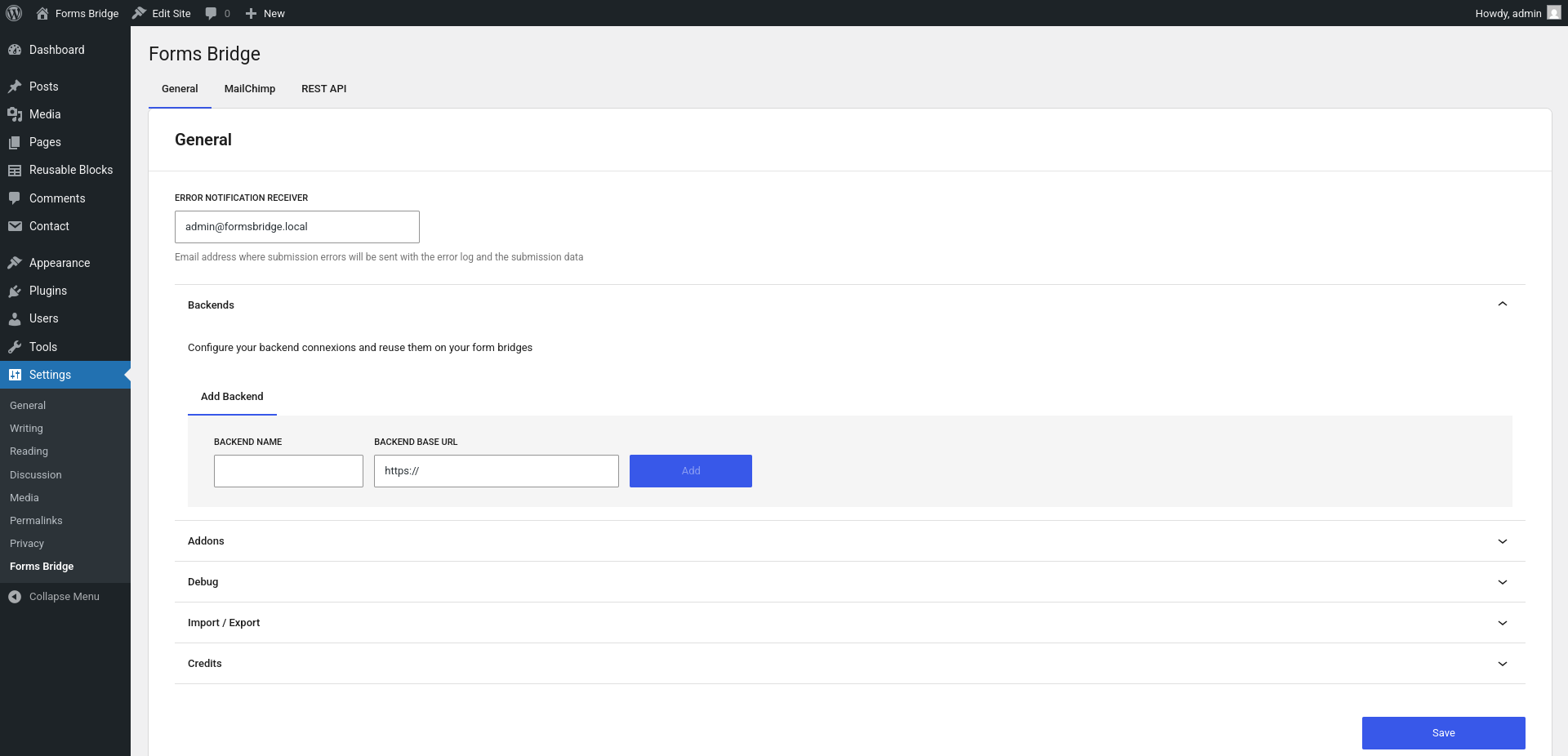
A backend is nothing more than a URL, an array of headers and a unique name to identify it. Start by typing a name and a URL and then click the Add button. Once done, you can add more headers to your backend connection.
A good practice is to use your backend URL domain as the backend URL, without path and use the path as part of your bridge endpoints!
In this example, we will work with ntfy, a simple HTTP-based pub-sub notification service. With backend headers we can set the ntfy notification title, priority and tags, in addition to the content type of our message.
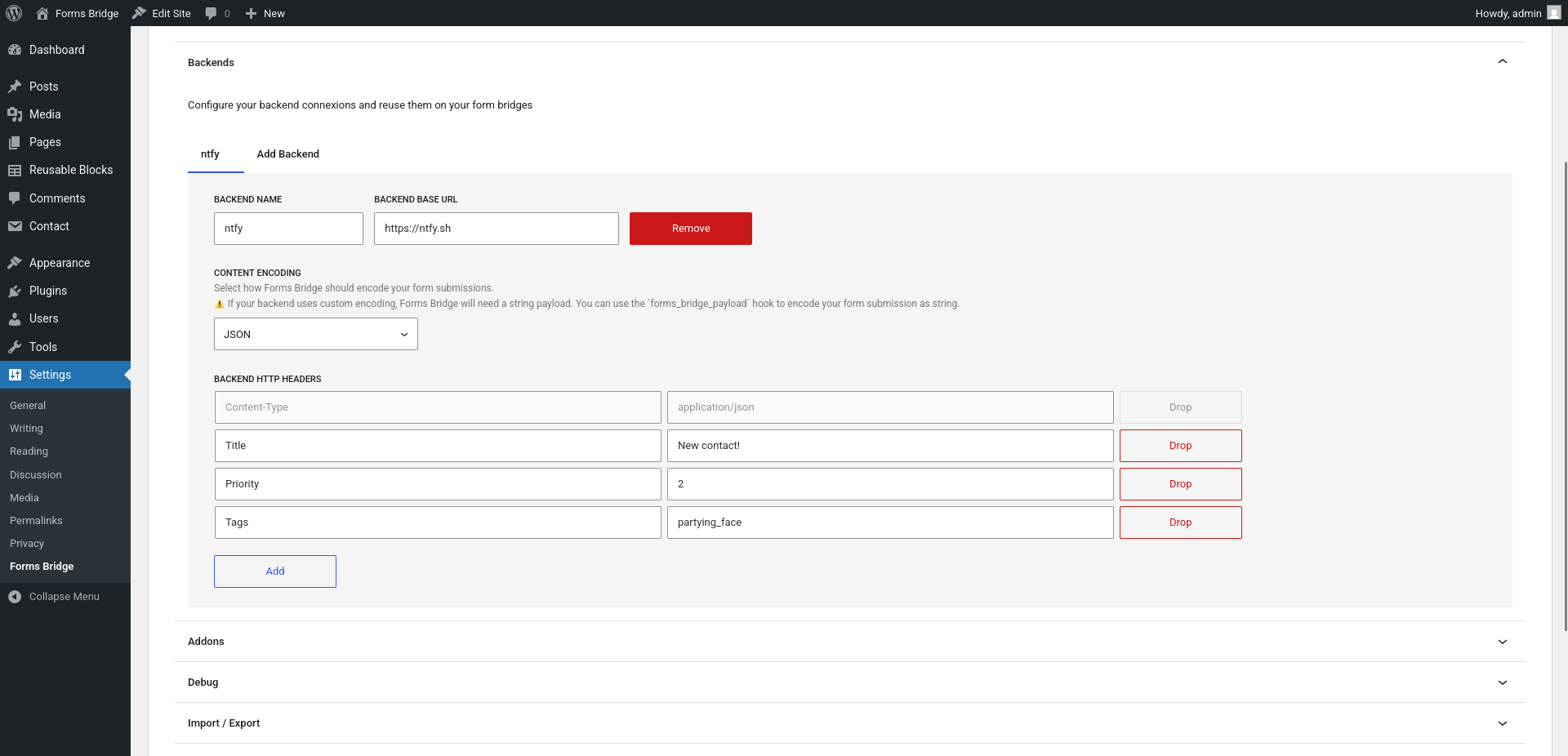
Bridge your form
Once you have your backend connection configured, you can start using it on your bridges. Let’s bridge our contact form to ntfy. Go to the REST API tab and create a new bridge. A bridge needs a unique name, a form and a backend. Depending on the type of API you work with, the bridge will need some extra fields. For example, for the REST API bridges, it’s required an endpoint and an HTTP method.
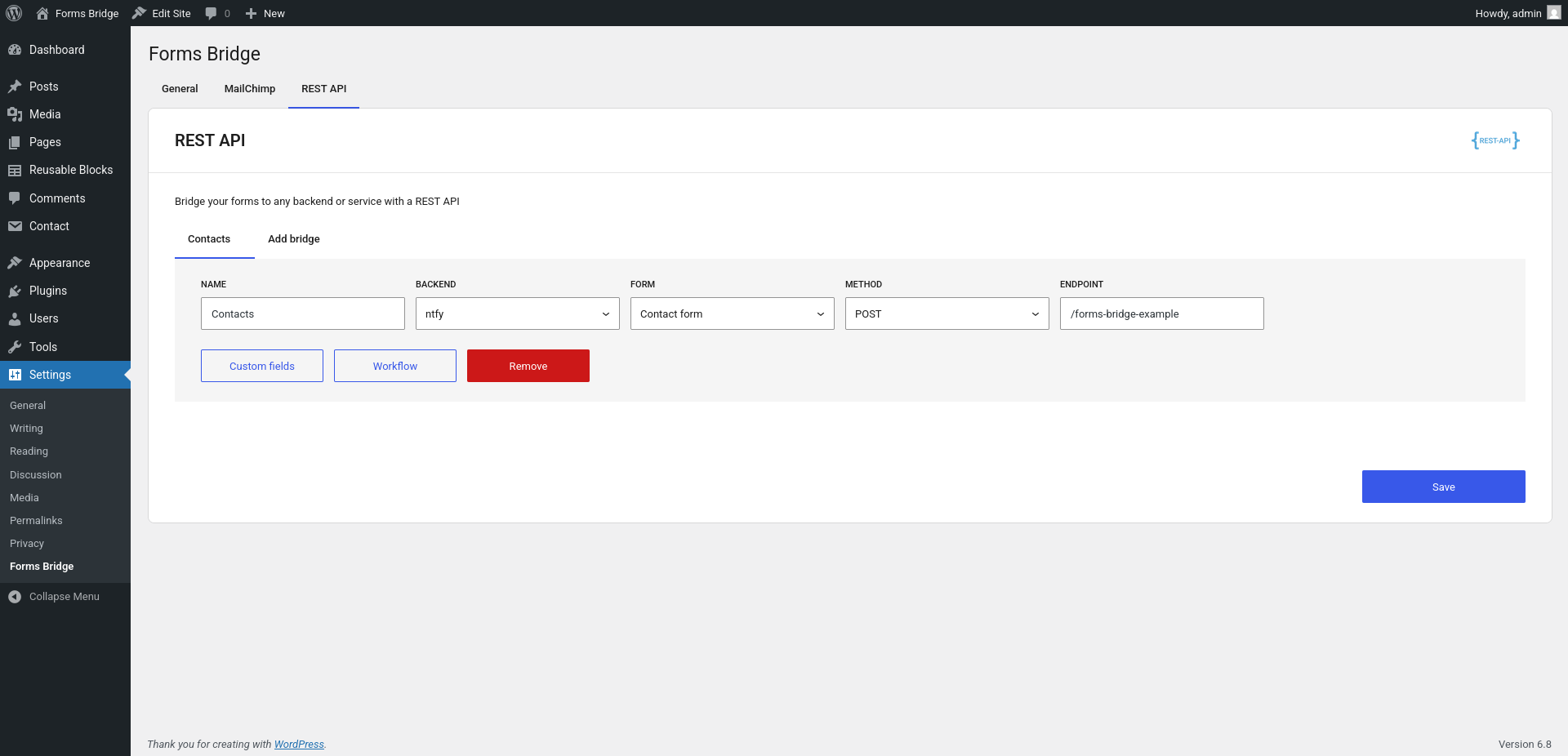
In our example, we’ve set Contacts as the name of the bridge, and bridged our contact form to the /forms-bridge-example endpoint of the ntfy backend using the POST method. After that, we got our first bridge 🎉.
Now, if someone fills up our contact form, a notification will be received on the forms-bridge-example topic on ntfy. You can subscribe your devices to the topic and get notified every time a new form submission is placed on your web.
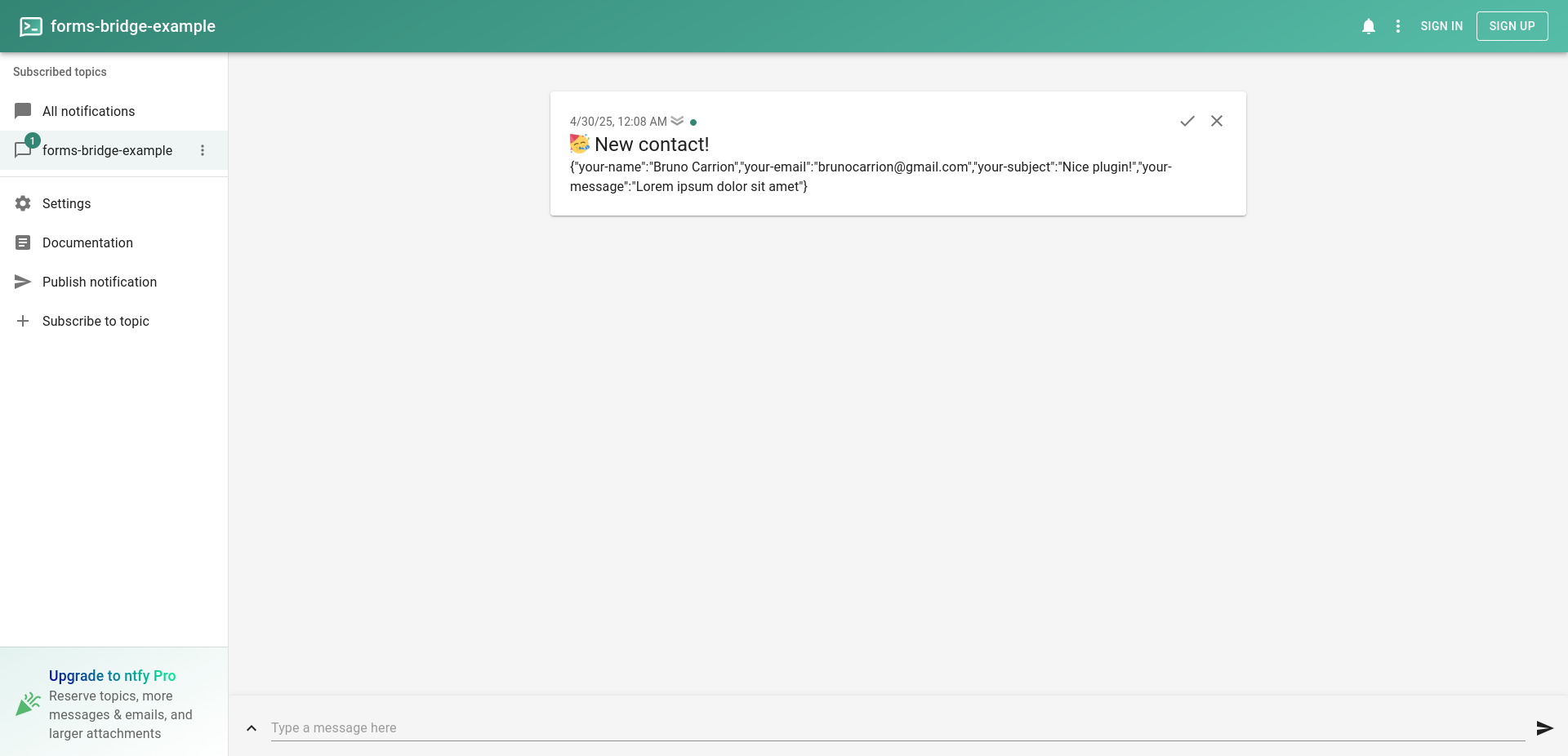
This is a basic setup. With this as a starter point, now you can add custom fields to the bridge, or configure a workflow to process your data before it is sent. We will cover these subjects on the following chapters of the documentation.
Settings page
To get you to the settings page go to Settings > Forms Bridge on the admin page of your WordPress site. This page is where you can configure and create your form bridges.
General settings
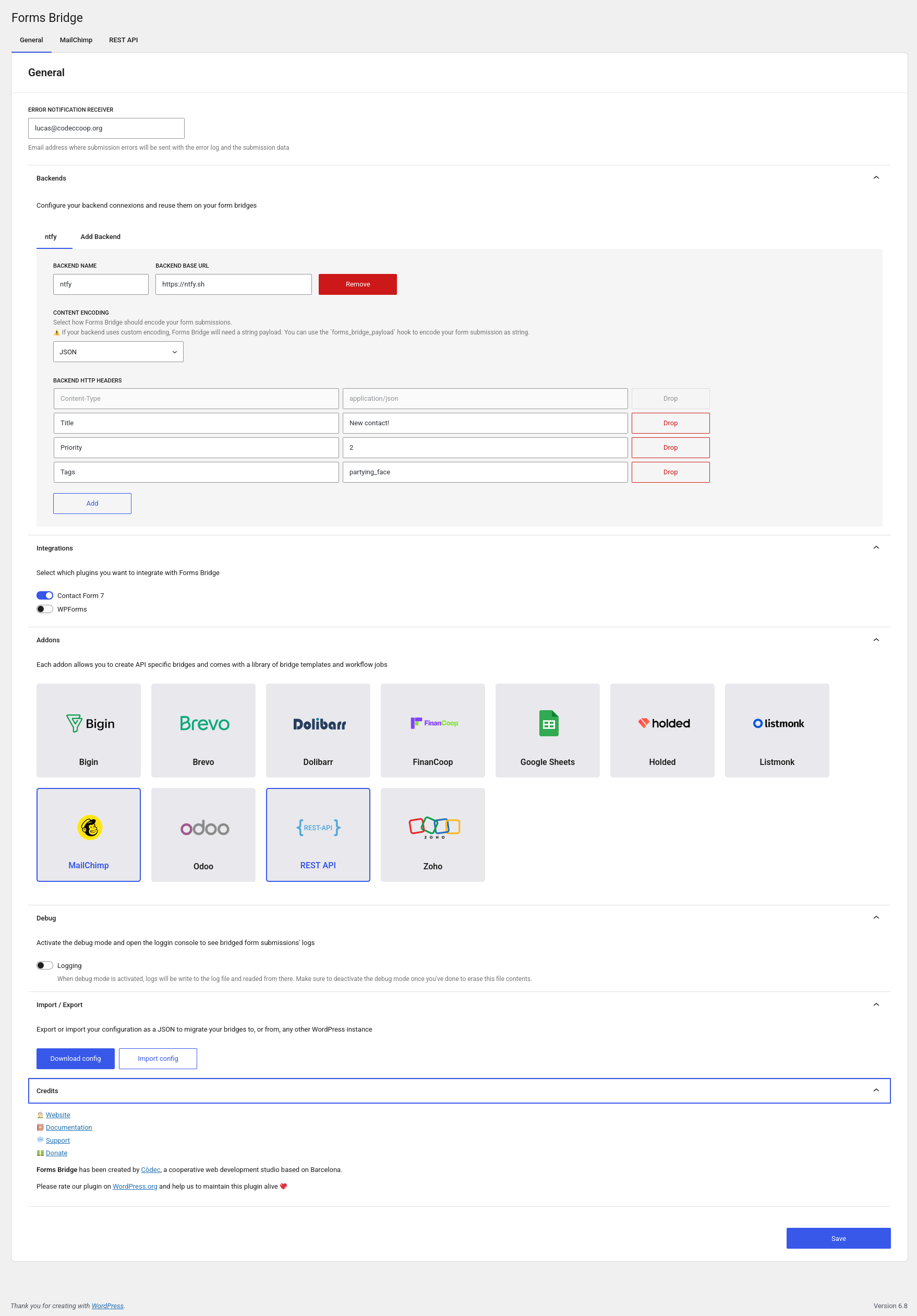
- Notification receiver: Email address where submission error reports will be sent.
- Backends: Backends are reusable and API independent. Configure your backends on the General tab and reuse them on your APIs tabs.
- Integrations: This panel is only visible if your WordPress instance has more than one integration (or none of them) and allows you to control with which integrations should Forms Bridge work.
- Addons: Activate and deactivate addons. Each addon open a new API tab, with new bridges, templates and workflow jobs. REST API addon is enabled by default.
- Debug: Activate the logging mode to open the console and get logs of your bridges in real time.
- Import / Export: Import or export your Forms Bridge configurations as JSON files and move it between instances with easy!
- Credits: Credits about the plugin and Còdec.
API tabs
Each time you activate a new addon, a new API tab will be visible on the settings page. Navigate to this tab and start bridging your forms to the addon’s API. To get more detail about addons, go the the addons chapeter.
Integrations
Integrations are well known plugins that add forms to WordPress. You can install Forms Bridge without any integration installed on your WordPress instance, but without one of the supported integrations, this plugin is useless, so take a look at our supported integrations and start by installing one of them, if you didn’t it already.
Once an integration is installed Forms Bridge will detect it automatically and gets its forms displayed on the settings page.
Forms Bridge can work with multiple integrations at the same time. To get more than one integration running in parallel, you only have to go to the settings page and choose with which of the installed plugins do you want to work with.
If you have only one integration installed, Forms Bridge will treat it as the active integration and hide the integrations panel on the settings page.
Available integrations
Help us to improve 💪
If you could choose a new integration for Forms Bridge, which one would you choose?
Backends
In Forms Bridge, a backend is a set of configurations that handles the connection information and credentials required to get your form submissions bridged over HTTP requests to a remote system. Go to Settings > Forms Bridge > Backends to configure your backend connections.
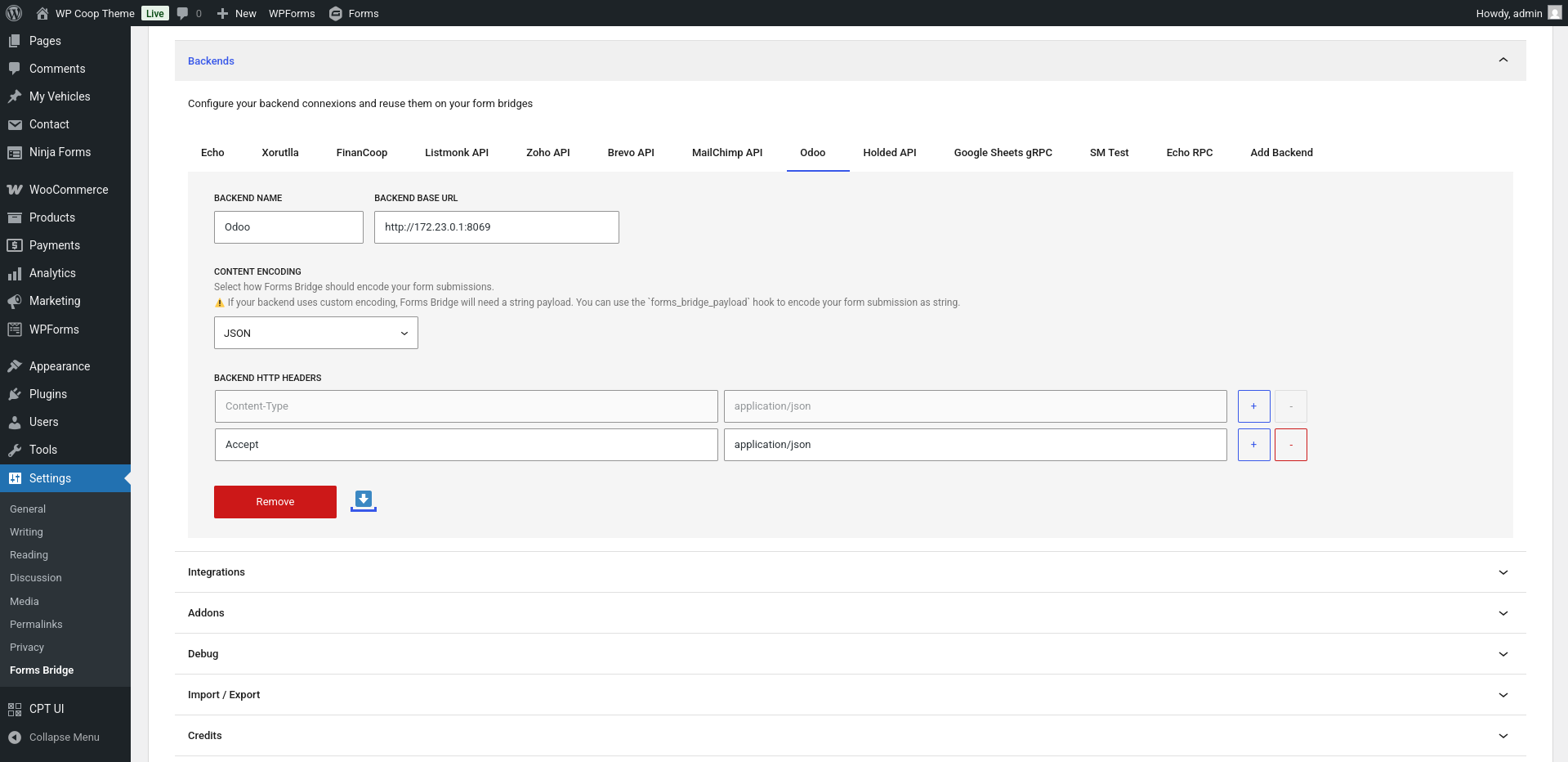
From the backends panel you can configure as many backend connections as you need. To create a new backend connection you have to set 3 fields:
- Name: A label to identify the backend. Backend names should be unique as it is the internal identifier Forms Bridge use to bind backends to bridges.
- Base URL: The base URL of your backend. The URL should start with http:// or https://. This base URL will be prepended to the bridge endpoint on runtime when a bridge is sending form submissions to your backend.
- Headers: An array of HTTP headers. The headers table will be visible once you have the backend registered. By default, this table will has the Content Type header. In addition, you can add as many headers as you want. Use headers to store backend credentials like API keys and other metadata required by your backend API.
The Content Type header is a special header on Forms Bridge because it controls how Forms Bridge will encode your form payloads on the HTTP requests’ body. This is the only required header of a backend connection. If your bridge needs a custom encoding schema, you can select the Custom encoding option and manually fill the header value. If this is the case, remember to use the forms_bridge_payload filter to encode your form submissions and return them as a string. See the filters API chapter for more information about this filter.
Bridges
Bridges are the core concept of the plugin. A bridge is a pipeline that connects WordPress forms with backends or services over HTTP requests. The bridge pipeline has two ends, the form on one hand, and the backend on the other. Form submissions data will go through the bridge pipeline from WordPress to the backend. In the process, you can add custom fields to the payload and manipulate the data on the bridge workflow.
A bridge is tied to an API, so to create bridges you need to have at least one addon enabled. Each Forms Bridge addon comes with a new bridge class with the ability to communicate with the respective API. Forms Bridge have REST API bridges enabled by default.
Custom fields
Custom fields are data that will be added to the bridge payload on runtime. Use them to store private data you don’t want to place on your public forms, like user emails, or config values, like product IDs or lead tags.
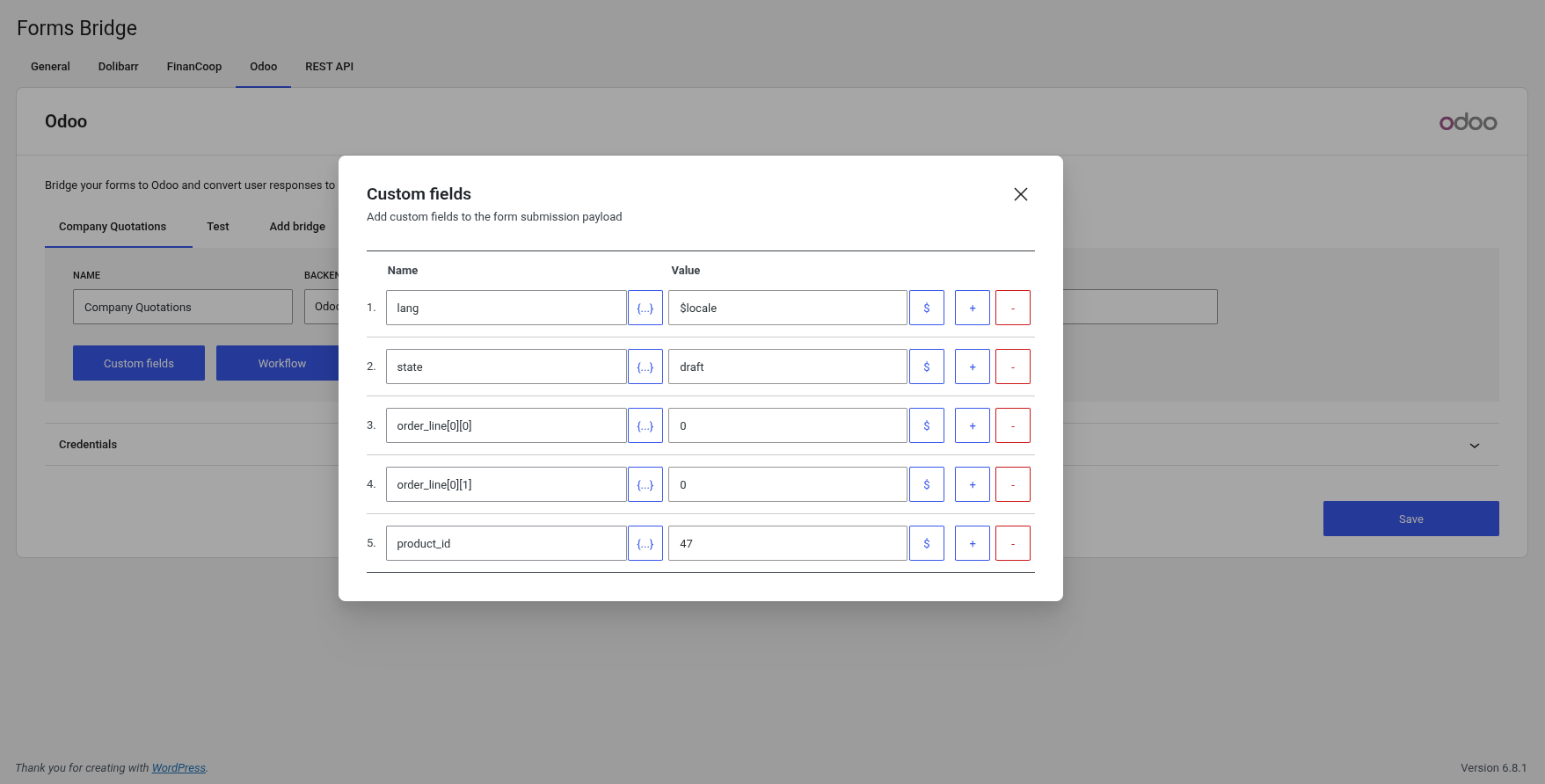
Each bridge has its own custom fields. A custom field is a pair of key-value, with the name on the left side, and the value on the right. Click on the Custom fields button of a bridge to open the fields table.
Custom fields are added to the payload before the bridge workflow start, so you can access this data on the workflow jobs.
If it is possible, Forms Bridge will introspect the bridge API schema each time the custom fields panel is opened. This introspection will return the list of the API endpoint fields. To access this list simply click on the {…} button and select an option to set its value as the field name. With this feature, Forms Bridge helps to map your submission fields to the API schema.
The API introspection only works with well known APIs.
REST API bridges does not performs this introspection because it’s an abstract bridge not tied to any specific API. If the introspection can’t be done, the button will be disabled.
For the values, you can define constant values –simply type it on the value input of the field–, or make use of meta tags. Each meta tag will be replaced with its context value on runtime. Click on the $ button to see all available tags. You can add more than one tag to the field value, or combine tags with strings into a composed value.
Available meta tags
| Meta tag | Description |
|---|---|
| $form_id | ID of the submission source form |
| $submission_id | ID of the form submission |
| $site_title | WordPress site title |
| $site_description | WordPress site description |
| $site_url | WordPress URL address |
| $admin_email | WordPress admin email address |
| $wp_version | WordPress instance version |
| $ip_address | IP address of the user |
| $referer | URL of the page where the form submission comes from |
| $user_agent | User agent of the browser of the user |
| $browser_locale | Accept-Language header value of the browser request |
| $locale | Locale of the page where the form is displayed. |
| $language | Language name of the page locale |
| $datetime | Submission datetime in Y-m-d H:m:s format |
| $gmt_datetime | Submission GMT datetime in Y-m-d H:m:s format |
| $timestamp | Submission timestamp |
| $iso_date | Submission datetime in ISO 8601 format |
| $gmt_iso_date | Submission GMT datetime in ISO 8601 format |
| $user_id | With active user sessions, ID of the user |
| $user_login | With active user sessions, name of the user |
| $user_name | With active user sessions, name of the user |
Workflows
With workflows you can combine multiple jobs to mutate your form submissions before them were sent over the wire to your backend.
The workflow input is the form submission and the output is the bridge payload. If you don’t set up a workflow, the form submissions without mutations will be used as bridge payloads.
A job is a function that runs on the backend and receives the payload as input and returns the payload with mutations as the output. In addition to data mutations, jobs can perform actions like databases writes or backend requests.
Each addon comes with a predefined set of jobs you can combine to set up your custom workflows. In addition, you can register your own workflow jobs. Take a look to our tutorial about how to register custom workflow jobs.
A workflow can have an arbitrary number of jobs. The submissions will go through the jobs in a sequential order, from the first job to the last one. The output of the last job will be the bridge’s payload.
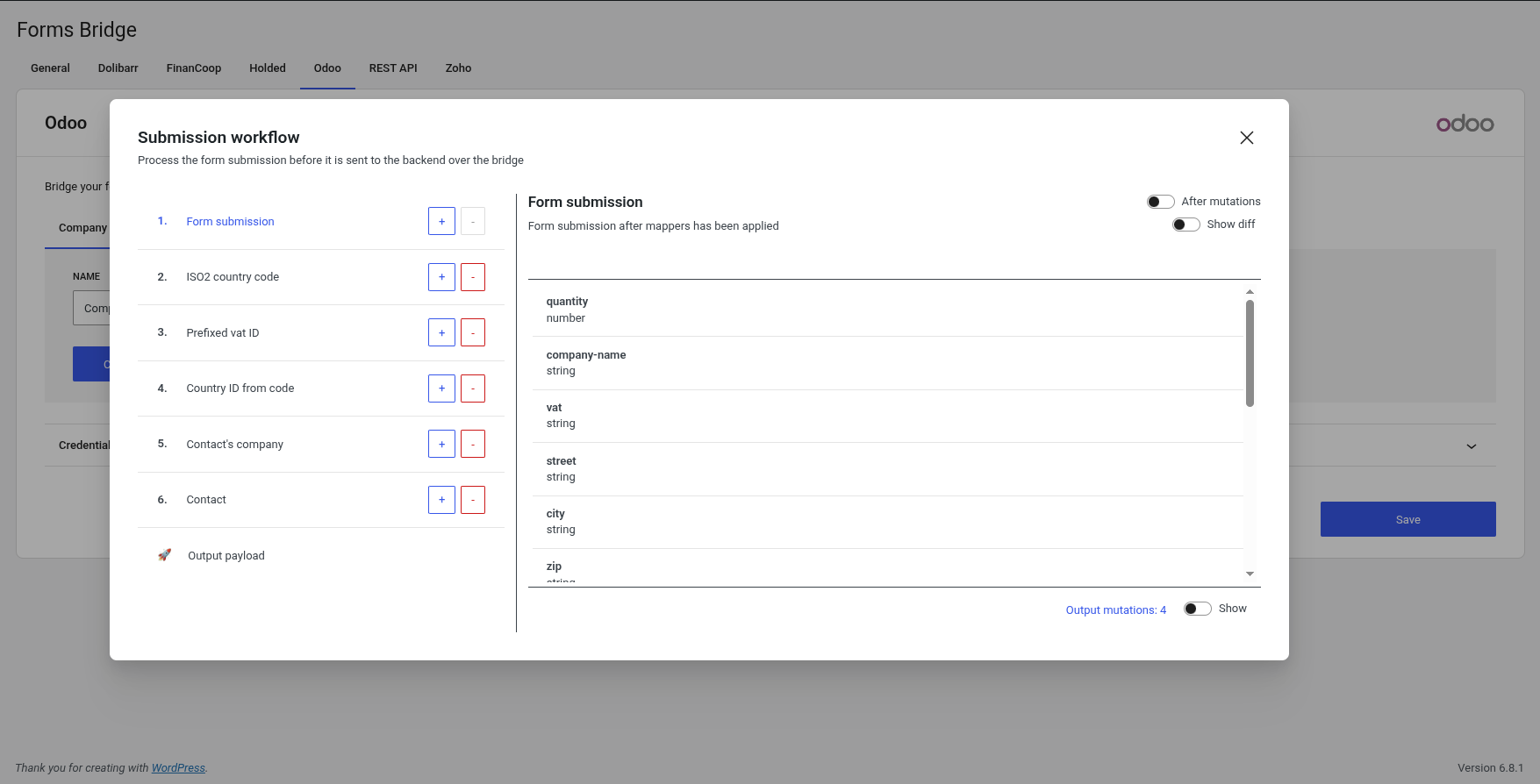
To set up a bridge workflow go to your bridge and click on the Workflow button to open the workflow panel.
The panel is divided in two columns: On the left side you can add, remove or replace jobs from the line. On the right, the panel will show you the current job title, description, fields interface and a representation of the payload schema at this point of the workflow.
By default, a workflow line has one step called Form submission. This step is the start point of every workflow.
The last item of the workflow line is the Output payload step. Go to this step to inspect the schema of the output payload.
Between the form submission and the output payload step, you can add workflow jobs. To add a new job to the chain, the output of the previous step has to fit the next job interface. The job interface is a declaration of required fields and its data types. If the input payload does not fit this interface, the job will be skipped.
To the output of each job it is possible to apply mutation layers to transform the output structure to fit the next job interface, or the backend API interface if it is the latter.
As in the custom fields table, in the mutation layers table you can use the introspection API of Forms Bridge to get information about the fields schema of the bridge endpoint. Simply click on the button {…} to get a list of all its fields and its types.
Mutation layers
Mutation layers are part of the workflow module but it deserve its own chapter. A mutation layer is a mapping from one field to a new one with a value mutation pipe.
With mutation pipes you can transform the field value. There are three types of mutation pipes:
- Type mutations: With type mutations you can transform your value type to one basic type to another, like string to integer conversions.
- Implode mutations: With implode mutations you can combine multiple values from a data structure into one composed string.
- Structure mutations: With structure mutations you can transform your submission structure by adding, removing or renaming its attributes.
Mutation layers works as a chain of mutations applied sequentially to the submission payload. This means that for each new mutation layer you add to the chain, its input is the result of the output of the previous layer. Take a look at our Deep dive into mutation layers tutorial to see this behavior in action with some examples.
You can apply mutation layers to every workflow job output. To set up mutation layers you have to open the workflow panel, go to the desired job step and click on the Show output mutations toggle button on the bottom right corner.
When you activate the output mutation layers mode, a table with mutations will be visible. Use this table to add as many mutation layers as you want to the payload.
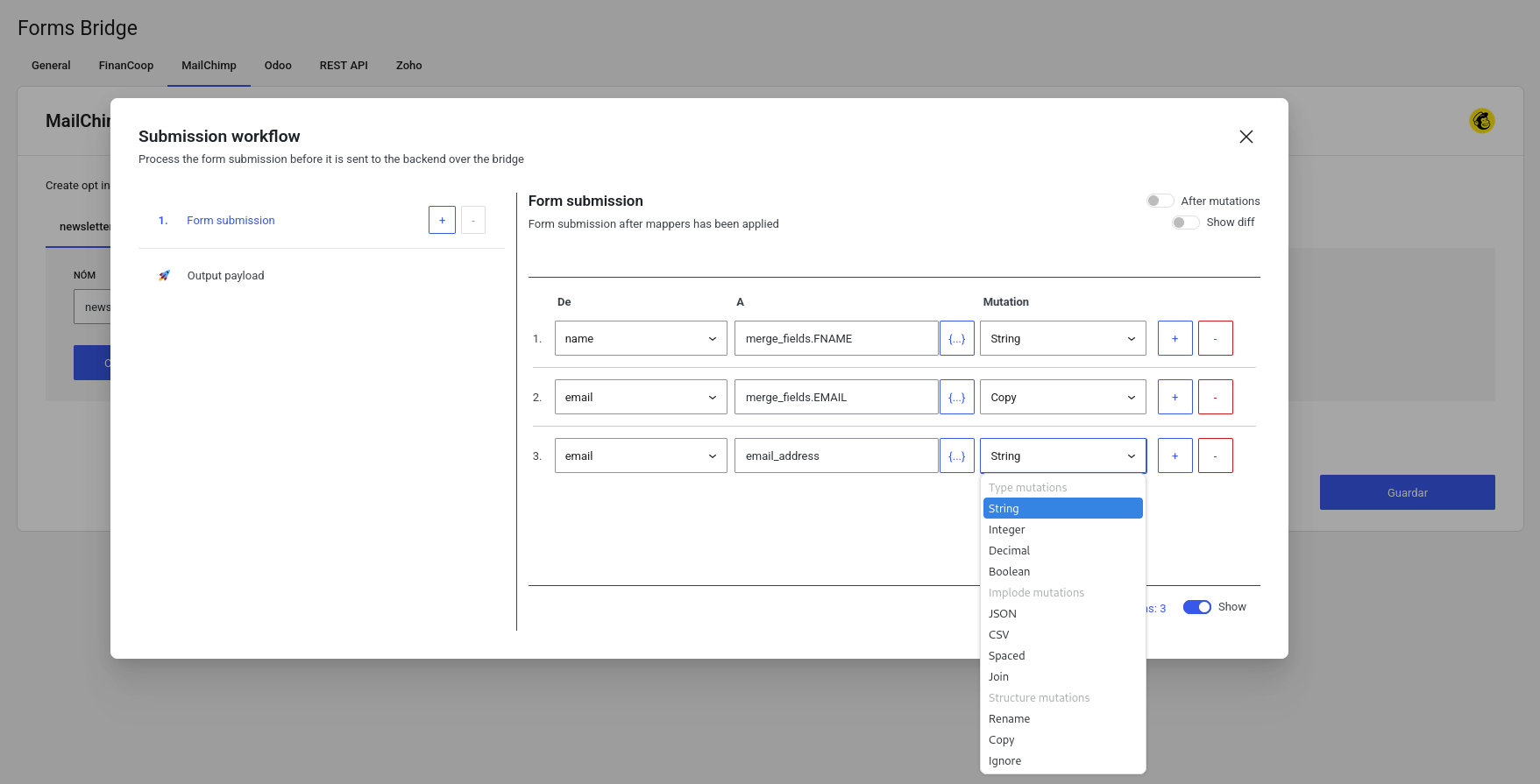
Take a look at our Deep dive into mutation layers tutorial if you want to realize the full potential of mutation layers in combination with json fingers.
Templates
Templates are blueprints of bridges you can use to set up your form integrations. To use a template go to the Add bridge tab of your addon and click on the Use a template button. After that, the template wizard will be displayed.
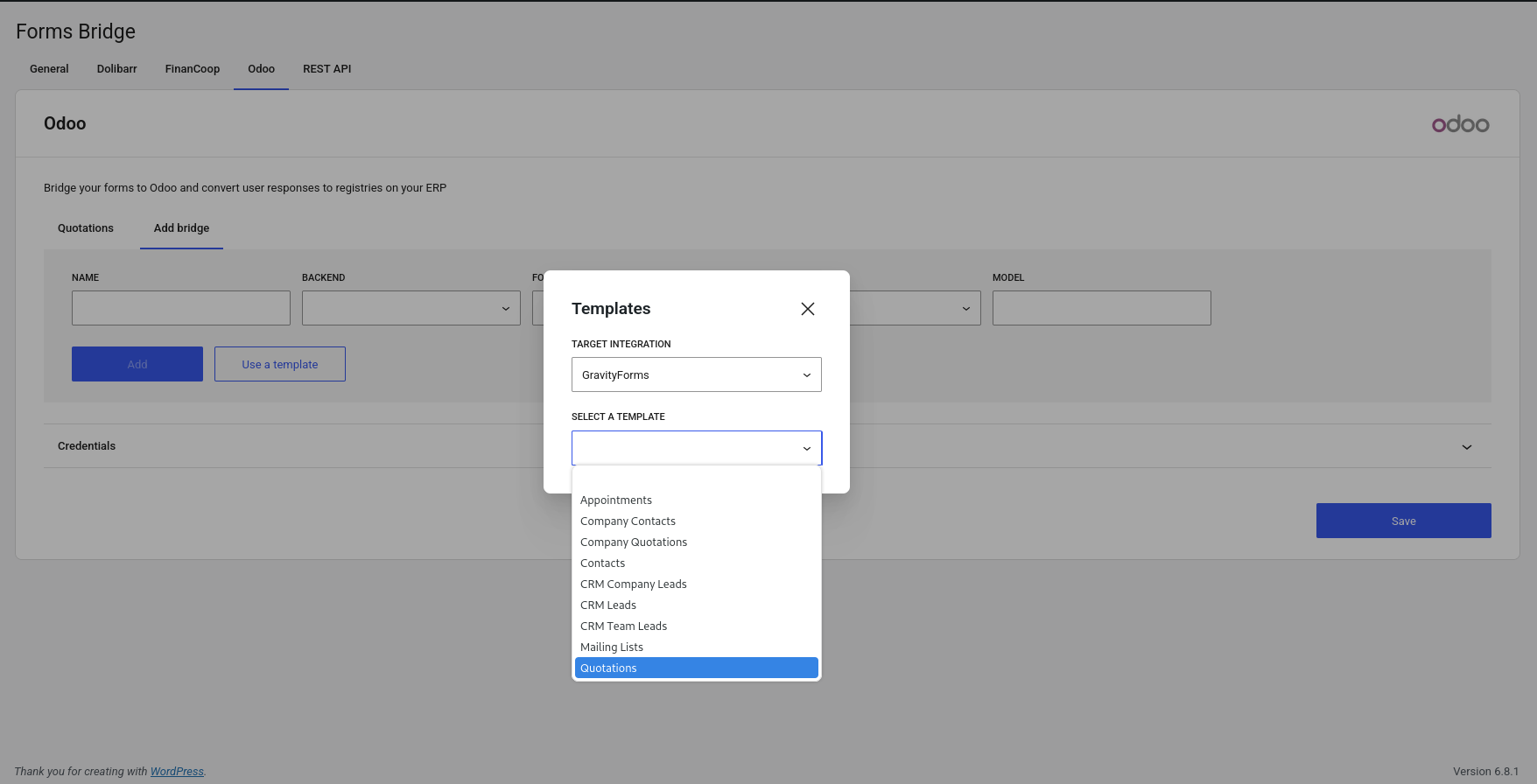
The first step is to choose an integration (if you have more than one) and a template to use. The integration is the plugin with which you want to create the new form and the template the blueprint of this form. In addition, the template wizard will ask you for required settings to setup the backend, if required, some kind of credentials, and the bridge.
The exception of WooCommerce templates.
With WooCommerce you can’t create forms. At the same time, the checkout form of WooCommerce is one of the most famous forms of WP, and most used! For this reason, Forms Bridge support WooCommerce as an integration, but with a special type of bridge templates. This kind of templates doesn’t create new forms, but a bridge setup that connects WooCommerce order placements with your backends.
Each addon has its own templates to solve common use cases of its API. Open the templates selector to see all options and choose one. After that, the wizard will guide you on the process.
The 3 (+1) steps of the template wizard are:
- Backend: Setup a new backend connection or reuse an existing one. On this step Forms Bridge performs a ping request to check the connection health before it lets you go forward.
- Form: Fulfill required fields to complete the form blueprint and convert it to a new form. The form will be created after the template submit.
- Bridge: With the backend and the form ready, the wizard will ask you for the bridge. Each bridge’s wizard will ask you for different kind of information to set up the bridge.
To finish the process click on the submit button and a new bridge will be created! If you didn’t reuse a backend connection or a form, these ones will be already created. The new bridge will bind the form with the backend in a ready to use bridge.
The +1 step is the credential step of the wizard. For certain APIs, like Odoo or Zoho, their bridges requires an additional piece of information, the credential. If that is the case, to the three steps enumerated before, it will be an additional step which will ask you for this credential data.
With templates you can get ready to use bridges. You can achieve the same result doing it manually, but with templates you can save a lot of time! We strongly recommend you to check for templates before start creating new bridges, and use them as starter point if your use case its not completely covered by the template result.
Json fingers
A json finger is a hierarchical pointer to data structures like children[0].name.rendered.
Json fingers are used by Forms Bridge as field names to allow the user to manipulate complex data structures on the form submission payload processing.
The syntax is inspired on the JSON standard, hence the name. If JSON is unknown to you, start by reading about the JSON syntax and then, a good playground to learn the concept is the jsonpathfinder project, give it a whirl.
Json fingers are used on custom field names and on mutation layers. If your json finger is simple (without path hierarchy), it works as a simple field name, but a the same time, you can break the name into hierarchy levels to create nested objects or items on an array.
For example, if your backend waits for an payload like this:
{
"name": "Bob",
"address": {
"street": "Carrer de Balmes, 250",
"city": "Barcelona"
}
}Then you can use address.street and address.city fingers to point to this nested attributes.
Use them as custom field names to add nested attributes, or as mutation layer target names to transform your plain form submissions into nested data structures.
Take a look at our Deep dive into json fingers tutorial if you want to realize the full potential of the json finger syntax.
Addons
Forms Bridge comes with free addons. Each addon adds to the plugin new bridges to work with specific APIs, new workflow jobs and bridge templates.
By default, Forms Bridge has the REST API addon enabled. This is the generic addon, with an abstract bridge not tied to any API and with which you can set up bridges to work with any API that implements the REST standard.
Because the REST API addon is intended to be abstract, it does not come with any template or workflow job. Use this kind of bridges to work with your custom APIs.
In addition to the REST API addon, there is other addons tailored to work with specific APIs. To enable or disable this addons, go to Settings > General > Addons and select which ones you want to enable.
Below you can access the documentation for each one of theme:
API
Forms Bridge has an open API of filters and methods to allow developers to extend Forms Bridge features with PHP. In this chapter we will cover the most interesting of them from the point of view of the developers who wants to integrate their themes or plugins with Forms Bridge.
It isn’t an extensive documentation of the Forms Bridge API. If you want a more in depth knowledge, you can browse the plugin’s code on the gitlab repository 🦊.
Getters
forms_bridge_form
Gets the current submission form.
Arguments
mixed $defaultDefault filtered value.integer $form_idIf declared, try to return form by ID instead of the current form.
Return
array|nullForm data or null.
Example
$form_data = apply_filters('forms_bridge_form', null);
if (!empty($form)) {
# do something
}forms_bridge_forms
Gets available forms.
Arguments
mixed $defaultDefault filtered value.string $integrationIf declared, filters available forms by integration slug.
Return
arrayAvailable forms as list of form data.
Example
$forms_data = apply_filters('forms_bridge_forms', []);
foreach ($forms_data as $form_data) {
# do something
}
forms_bridge_bridges
Gets available bridges for the current form.
Arguments
mixed $defaultDefault filtered value.string|int $form_idIf declared, returns bridges from the form with this id. This id should includes the integration slug as prefix if there is more than one active integration.string $integrationIf declared, filters bridges by API slug.
Return
arrayList of given form available bridge instances.
Example
$bridges = apply_filters('forms_bridge_bridges', [], 'wpcf7:31');
foreach ($bridges as $bridge) {
# do something
}forms_bridge_submission
Gets the current form submission.
Arguments
mixed $defaultDefault filtered value.
Return
array|nullCurrent form’s submission data.
Example
$submission = apply_filters('forms_bridge_submission', null);
if ($submission) {
# do something
}forms_bridge_uploads
Gets the current form’s submission uploaded files.
Arguments
mixed $defaultDefault filtered value.
Return
array|nullCurrent form’s submission uploaded files.
Example
$uploads = apply_filters('forms_bridge_uploads', null);
if ($uploads) {
# do something
}
forms_bridge_backends
Gets the registered backend connection settings.
Arguments
mixed $defaultDefault filtered value.
Return
arrayList with registered backend settings data.
Example
$backends = apply_filters('forms_bridge_backends', []);
foreach ($backends as $backend) {
# do something
}
forms_bridge_backend
Gets a backend connection settings by name.
Arguments
mixed $defaultDefault filtered value.string $nameName of the backend.
Return
array|nullIf found, backend connection settings data.
Example
$backend = apply_filters('forms_bridge_backend', null);
if ($backend) {
# do something
}
Filters
forms_bridge_payload
Filters the submission data to be sent to the backend. If the payload is returned as an array of data, Forms Bridge will encode it as string based on the Conent-Type header of the backend before it is sent.
Arguments
array $payloadSubmission payload.Form_Bridge $bridgeBridge instance.
Return
array|string|nullFiltered payload. If null is returned, bridge submission will be skipped.
Example
add_filter('forms_bridge_payload', function ($payload, $bridge) {
return $payload;
}, 10, 2);forms_bridge_attachments
Filters attached files to be sent to the backend. Attachment files are only supported by backends with multipart/form-data value of the Content-Type header. Otherwise, Forms Bridge will encode the files as base64 strings and append it to the payload.
Arguments
array $attachmentsSubmission attached files. An attachment is a key value pair with the attachment name and the path to the file.Form_Bridge $bridgeBridge instance.
Return
arrayFiltered attachments.
Example
add_filter('forms_bridge_attachments', function ($attachments, $bridge) {
return $attachments;
}, 10, 2);forms_bridge_backend_headers
Filters the bridge HTTP request headers. The array contains the backend custom headers and a set of default backend headers. Fired on each form bridge submission.
Arguments
array $headersAssociative array with HTTP headers.Http_Backend $backendBackend instance.
Return
arrayFiltered HTTP headers.
Example
add_filter('forms_bridge_backend_headers', function ($headers, $backend) {
return $headers;
}, 10, 2);forms_bridge_backend_url
Filters bridge submission request URL. The URL is the result of the concatenation of the backend base URL and the bridge endpoint. Fired on each form bridge submission.
Arguments
string $urlSubmission request URL.Http_Backend $backendBackend instance.
Return
arrayFiltered HTTP headers.
Example
add_filter('forms_bridge_backend_url', function ($url, $backend) {
return $url;
}, 10, 2);forms_bridge_request
Filters the backend request params before it is sent. Forms Bridge use the WP_Http under the hood. Check out the WP_Http::request documentation for more details about the params.
Arguments
array $paramsHTTP request params.
Return
arrayFiltered HTTP request params.
Example
add_filter('forms_bridge_request', function ($request) {
return $request;
}, 10, 1);forms_bridge_response
Filters the bridge request response.
Arguments
array|WP_Error $responseHTTP request response.
Return
array|WP_ErrorFiltered HTTP request response.
Example
add_filter('forms_bridge_response', function ($response) {
return $response;
}, 10, 1);forms_bridge_prune_empties
Controls if Forms Bridge should clean up the submission data and prune its empty fields.
Arguments
boolean $pruneTrue by default, use this filter to avoid the payload prune.Form_Bridge $bridgeBridge instance.
Return
booleanTrue value will trigger a prune of the empty values of the submission payload. An empty value is a null value or an empty string.
Example
add_filter('forms_bridge_prune_empties', '__return_false');forms_bridge_skip_submission
Controls if Forms Bridge should skip the form submission.
Arguments
boolean $skipFalse by default, use this filter to skip bridge submissions.Form_Bridge $bridgeBridge instance.
Return
booleanTrue value will skip the bridge submission.
Example
add_filter('forms_bridge_skip_submission', function ($skip, $bridge) {
if ($bridge->name === 'skip') {
return true;
}
return $skip;
}, 10, 2);forms_bridge_woo_trigger_submission
Controls if Forms Bridge should trigger the bridge submission on each order status change.
Arguments
boolean $triggerTrue if new status iscompleted, false otherwise.integer $order_idID of the current order.string $new_statusNew order status.string $old_statusOld order status.boolean $is_bridgeBoolean value that tracks if the order has been already bridged.
Return
booleanTrue value will trigger the bridge submission.
Example
add_filter('forms_bridge_woo_trigger_submission', function ($trigger, $order_id, $new_status, $old_status, $is_bridged) {
if ($old_status === 'processing' && !$is_bridge) {
return true;
}
return $trigger;
}, 10, 5);forms_bridge_skip_error_notification
Controls if Forms Bridge should skip the error email notification.
Arguments
boolean $skipFalse by default, if return as true email notification will be skipped.WP_Error $errorInstance of the catcher error.Form_Bridge $bridgeCurrent bridge instance.array $payloadCurrent bridge payload.array $attachmentsCurrent bridge attachments.
Return
booleanTrue value will skip the error email notification.
Example
add_filter('forms_bridge_skip_error_notification', function ($skip, $error, $bridge, $payload, $attachments) {
$error_response = $error->get_error_data()['response'];
if ($error_response['code'] === 401) {
return true;
}
return $skip;
}, 10, 5);Actions
forms_bridge_before_submission
Action to do just before submission has been sent to the backend.
Arguments
Form_Bridge $bridgeBridge instance.array $payloadPayload data.array $attachmentsAttachments list.
Example
add_action('forms_bridge_before_submission', function ($bridge, $payload, $attachments) {
# do something
}, 10, 3);forms_bridge_after_submission
Action to do after the submission has been successfully sent to the backend.
Arguments
Form_Bridge $bridgeBridge instance.array $responseRequest response data.array $payloadPayload data.array $attachmentsAttachments list.
Example
add_action('forms_bridge_after_submission', function ($bridge, $response, $payload, $attachments) {
# do something
}, 10, 4);forms_bridge_on_failure
Action to do after a bridge submission error.
Arguments
Form_Bridge $bridgeBridge instance.WP_Error $errorRequest error response.array $payloadPayload data.array $attachmentsAttachments list.
Example
add_action('forms_bridge_on_failure', function ($bridge, $error, $payload, $attachments) {
# do something
}, 10, 4);














